Due diligence is critical in commercial transactions, mergers, acquisitions, and investment choices. It requires a comprehensive examination of the target business or opportunity to ensure that educated judgements are made and any risks are mitigated. By systematically acquiring and analysing data, evaluating financial documents, and assessing the company’s operations and risk management, due diligence helps unearth important insights that might influence the outcome of an acquisition.
In this article, we’ll explain the due diligence process, explore its types, and share best practices for ensuring successful outcomes.
What is Due Diligence?
At its essence, due diligence is the practice of thoroughly investigating and confirming important information before completing a decision or engaging in a transaction. Whether acquiring a firm or making an investment, due diligence aims to take all reasonable steps to ensure that the decision is based on accurate and comprehensive information.
In practice, due diligence is a methodical procedure often carried out by a team of professionals with varied skills, from financial analysts to legal consultants. The idea is to uncover both dangers and opportunities while enabling purchasers or investors to make educated choices. This approach is vital to avoid unforeseen issues and enhance the chances for success in any deal.
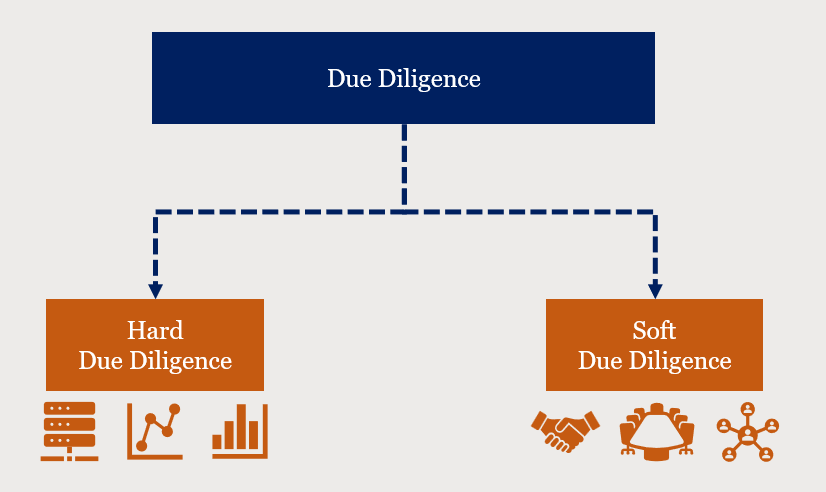
Types of Due Diligence
There are two primary types of due diligence: hard due diligence and soft due diligence. Each serves a distinct function but is equally important in understanding the target company comprehensively.
1. Hard Due Diligence
Hard due diligence focuses on tangible, quantifiable data. This aspect of due diligence is primarily concerned with the target company’s financial health, operations, and tax obligations. It involves reviewing financial statements, tax returns, contracts, and business transactions.
Hard due diligence ensures that every number and contract is verified and thoroughly analysed. This helps identify any red flags, such as liabilities, outstanding debts, or operational inefficiencies.
2. Soft Due Diligence
Soft due diligence examines a company’s less measurable features, such as its management, culture, and critical business relationships with partners, suppliers, and consumers. Hard due diligence is mostly focused on the numbers.
Although softer, more subjective due diligence is still essential. It assists in locating any management errors, cultural conflicts, or deficiencies in the organisation’s capacity for innovation, research, and intellectual property.
The Due Diligence Process
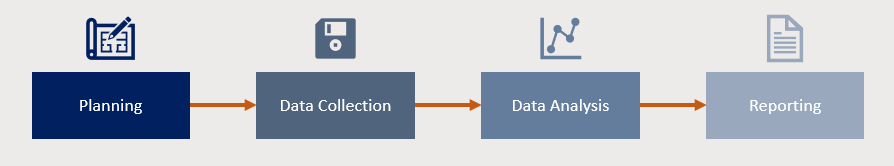
The due diligence investigation process usually involves several phases: planning, data collection, data analysis, and reporting. Each stage is critical to ensuring that the process is both thorough and accurate.
- Planning: In this phase, the scope of due diligence is defined. The goals and focus areas are established, such as financial health, legal compliance, or operational efficiency. A clear plan is essential to avoid missing critical elements.
- Data Collection: This stage gathers all relevant information, including financial records, contracts, operational data, and more. This often involves working closely with the target company to access the necessary documents in mergers or acquisitions.
- Data Analysis: Once the data is collected, experts analyse it to identify potential risks, liabilities, and opportunities. This is the most critical part of the due diligence process, as it reveals any financial inconsistencies, legal issues, or operational inefficiencies.
- Reporting: Finally, the findings are compiled into a comprehensive report summarising the key risks and opportunities. This report helps decision-makers understand the full picture and decide whether to proceed with the transaction.
Due Diligence in M&A Transactions
Due diligence is a fundamental step in mergers and acquisitions (M&A). These transactions involve not just the exchange of money but also the integration of operations, cultures, and strategies. During M&A due diligence, experts assess everything from financial health to intellectual property and innovation capabilities.
Financial due diligence is one of the most important parts of the entire procedure. It entails a thorough analysis of the target company’s financial documentation, including cash flow, debt levels, balance sheets, income statements, and tax returns. The company’s internal controls, accounting procedures, and general financial management are all assessed as part of financial due diligence investigations. Financial due diligence experts ensure that there are no financial surprises when the deal closes. This factor is crucial when it comes to large-scale investments, mergers, and acquisitions, where financial soundness is a top priority.
It’s also critical to comprehend how a corporation does business with its partners, suppliers, and customers. Low customer retention rates or strained supplier relations might considerably impact the company’s post-acquisition value. In M&A, due diligence ensures that no undiscovered risks could compromise the deal’s success.
Best Practices for Due Diligence
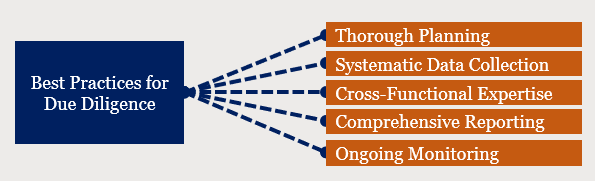
To conduct effective due diligence, companies should follow a set of best practices. These include:
- Thorough Planning: Clearly define the scope and objectives of the due diligence process.
- Systematic Data Collection: Gather all necessary data, leaving no stone unturned.
- Cross-Functional Expertise: Assemble a team of experts with financial, legal, and operational knowledge.
- Comprehensive Reporting: Summarise findings in a report highlighting risks and opportunities.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Even after the transaction is completed, regular monitoring is essential to identify potential risks early on.
Common Pitfalls in Due Diligence
Some common mistakes to avoid in due diligence include inadequate planning, rushing through data collection, and failing to identify potential risks. Overlooking key details can lead to missed opportunities or unanticipated problems later on. Companies and individual investors should ensure that their due diligence process is both thorough and methodical.
The Importance of Ongoing Monitoring
Avoiding frequent due diligence errors includes hastily gathering data, failing to recognise potential hazards and inadequate planning. Ignoring important details can result in lost chances with business partners or unforeseen issues down the road. Businesses need to ensure that their due diligence procedure is robust and systematic.
The Role of Technology in Due Diligence
Technology has transformed due diligence, increasing accuracy and efficiency. Cutting-edge equipment and software may improve teamwork, speed up data collection, and make it easier to analyse massive amounts of data. Even while technology can expedite diligence investigations to ensure informed judgment, it should always be used in concert with human expertise.
Artificial intelligence (AI), specifically, is transforming the due diligence process by improving accuracy, efficiency, and the ability to process large volumes of data. AI tools can quickly sift through financial records, contracts, and other documents, identifying patterns and anomalies that human reviewers may miss. A notable real-life example is JPMorgan’s use of AI to perform due diligence in its “COIN” (Contract Intelligence) program, which reportedly reduced the time spent reviewing loan documents from 360,000 hours to just seconds. By automating routine tasks and providing deeper insights through data analytics, AI accelerates due diligence and helps uncover hidden risks, enabling more informed decision-making in transactions such as mergers and acquisitions.
Conclusion
Due diligence is an essential part of any major business transaction. Businesses can make well-informed decisions by systematically reviewing financial records, assessing operations, and identifying potential risks. With the help of technology and ongoing monitoring, the business due diligence process continues to evolve—allowing companies to act swiftly while minimising risks.
Following best practices and assembling a team of skilled experts will ensure that your due diligence efforts lead to successful and sustainable outcomes.