What is a succession planning framework?
Succession planning is a systematic process designed to identify and assemble a pool of employees who are capable of filling positions that are critical to the effective functioning of a business and enable the delivery of strategic priorities. Whether you’re developing a succession plan as part of your exit strategy or handing control to a family member, setting a comprehensive framework will mitigate changeover risks and steady the future course of your business.
Building a strong foundation
Building a detailed human capital assessment framework is the foundation of succession planning. It will allow you to:
- Identify the critical roles and the skill sets required to excel in those roles;
- Identify the future leaders of the business to fill these roles and
- Set processes to nurture, develop and prepare the future leaders for these critical roles.
Identifying critical roles for succession planning
A thorough review of the business needs to be conducted to determine which positions, if left vacant, could create immediate operational, reputational or financial risks and/or compromise progress toward achieving the strategic priorities.
Each position should also consider the criticality and retention risk scale. On this scale, high-impact roles carry high retention risk because the individuals identified for these roles often have unique and sought-after skills. On the other end of the scale, low-impact roles tend to have a low retention risk due to the perceived notion that their skill sets are lower, widening the candidate pool available to fill that role. These steps will help identify those critical employees who require healthy challenges and support to maintain their engagement and focus on your business.
Identify the skill sets for the critical roles to develop successor assessment criteria
Once critical roles are defined, a competency-based assessment must be developed to create a success profile for each critical position that defines the current and future-oriented knowledge, skills, abilities, qualifications, and personal qualities required to excel in the role. These profiles serve as guidelines for evaluating potential successors and ensure a streamlined and objective assessment process.
Assessing and reviewing potential successors
Potential successors should be continuously assessed against the success profiles. This assessment can involve various tools such as 360-degree feedback, business simulations, cognitive assessments, and psychometric tests. The goal is to understand each candidate’s readiness, capabilities, and potential for taking on new roles. While conducting these assessments, individuals can be categorised using the 9-box model.
The 9-box model is a talent management tool widely used to segment employees into nine groups based on two dimensions: performance and potential. The model is designed to align talent management and development initiatives where employees can add the most value to the business.
An example is shown in Chart 1.
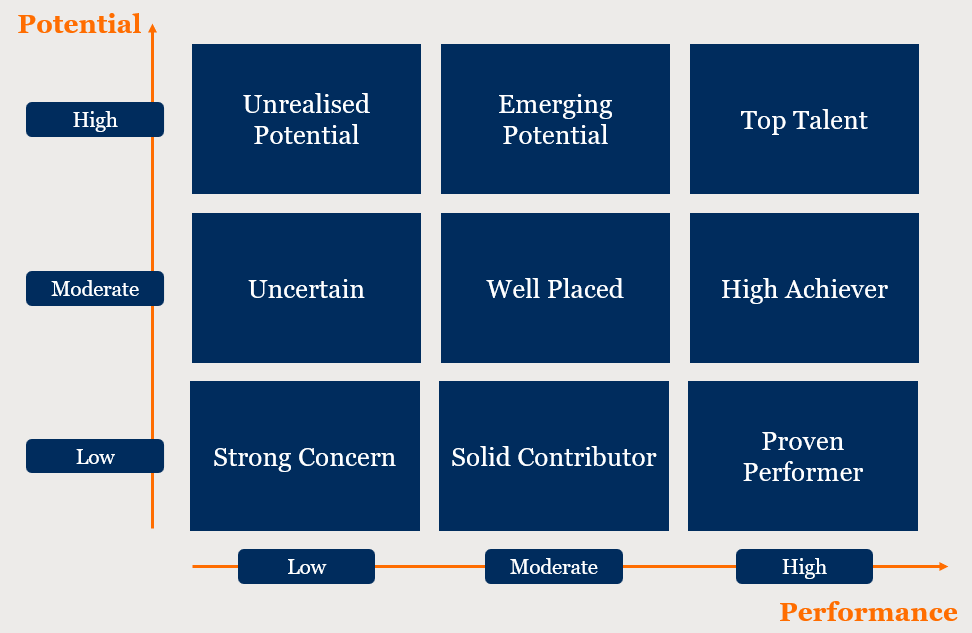
Chart 1: 9-Box Model Example
How to Interpret the 9-Box Model
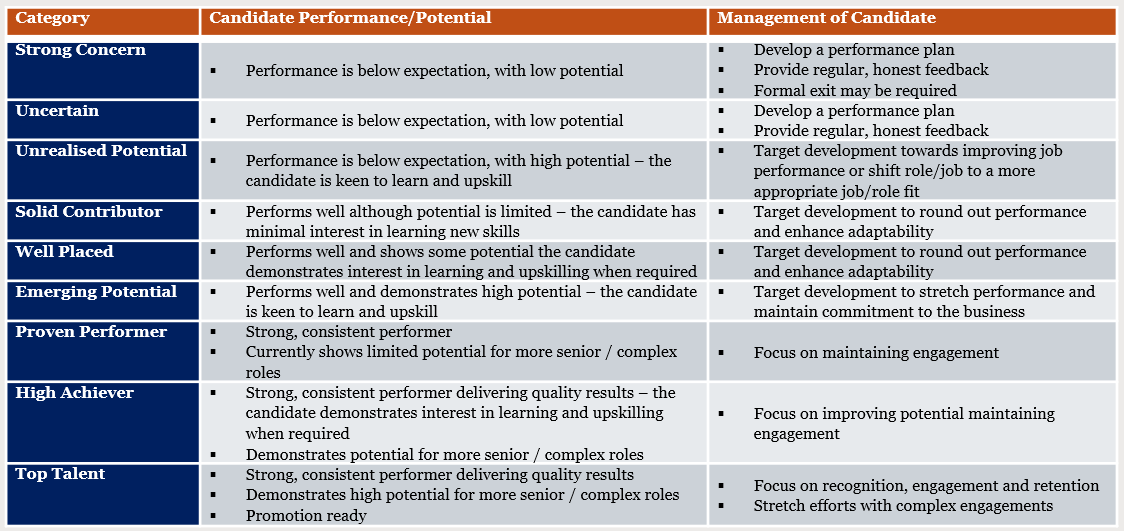
Developing Successors
Implementing development programs
Development programs catered to each critical role or potential successor should be created to provide the necessary support, training, and experiences to enhance their skills in preparation for future responsibilities. This step is crucial for nurturing and guiding individuals on their journey towards leadership positions. This should include creating the following:
- Training and development programs;
- Mentoring and coaching initiatives; and
- Leadership development programs.
During the development phase, clear and consistent communication and feedback are crucial in keeping all stakeholders informed and providing regular, timely feedback to shape and develop the critical roles’ required behaviours.
Knowledge Transfer and Risk Management
Identify and prioritise knowledge loss risks associated with critical roles. Capture at-risk knowledge and ensure it is documented and transferred to the potential successors. This step helps mitigate the impact of losing critical knowledge when key employees leave or are transitioned out.
Implementation and Transition Planning
Create a detailed implementation plan that outlines the steps and timelines for executing the succession plan. This plan should include regular reviews and updates to ensure its continued relevance and effectiveness. It should also involve key metric benchmarks for candidates based on various criteria.
Specialised Planning
Family-owned businesses often face unique and complex challenges when it comes to succession planning. These issues can significantly impact the smooth transition of management and ownership to the next generation. Here are some typical issues encountered:
- Family Conflicts
Conflict within the family is a common reason for failure during the succession process. Disputes can arise over various issues, including differing visions for the company’s future, compensation disputes, and the distribution of ownership shares.
- Lack of Preparedness
Many family businesses are ill-prepared for succession. This includes a lack of formal succession plans, insufficient training for the next generation, and a general unpreparedness of children to take over leadership roles.
- Financial Needs and Expectations
There can be conflicting financial needs between generations. For example, the older generation may rely on the sale of the business for retirement funds, while the younger generation may want to take over without a significant financial burden. Strategies like instalment sales or trusts can help mitigate these issues.
- Reluctance to Let Go
Founders often struggle to relinquish control of the business they build, which can create leadership uncertainty and hinder the transition process. This reluctance can be due to emotional attachment or financial dependency on the business.
- Lack of Professional Advice
Many family businesses do not seek professional advice for succession planning, which can lead to poorly structured plans that fail to effectively address both business and family dynamics.
- Unclear Roles and Responsibilities
Ensuring that heirs and leaders understand their roles clearly is crucial. Without a well-defined strategy, there can be confusion and inefficiency, jeopardising the business’s future.
- Vision and Values Misalignment
Conflicts over the company’s vision and values can create significant barriers. A shared vision and strong family values are essential for a successful transition, and these need to be fostered and reinforced over time.
- External Challenges
Family businesses also face external challenges such as globalisation, economic changes, and shifting consumer preferences, which can complicate the succession process further.
Addressing these issues proactively through comprehensive planning, clear communication, and professional guidance can help ensure a smoother transition and the long-term success of the family business.
The Bottom Line
Identifying the critical roles for succession planning is a key aspect of human resource management that helps businesses prepare for the future. By following these pointers, businesses can ensure that they have the right individuals in place to fill critical roles and can help minimise disruption risks in operations. By taking a proactive approach to succession planning, businesses can build a strong and resilient workforce that is ready to meet the challenges of the future.



